Eosinophilic Esophagitis

Summary
What is eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE)?
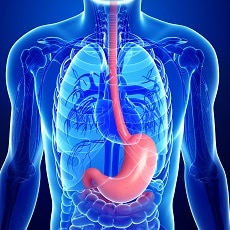
Eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) is a chronic disease of the esophagus. Your esophagus is the muscular tube that carries food and liquids from your mouth to the stomach. If you have EoE, white blood cells called eosinophils build up in your esophagus. This causes damage and inflammation, which can cause pain, trouble swallowing, and food getting stuck in your throat.
EoE is rare. But because it is a newly recognized disease, it is being diagnosed more often. Some people who think that they have reflux (GERD) may actually have EoE.
What causes eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE)?
Researchers are not certain about the exact cause of EoE. They think that it is an immune system/allergic reaction to foods or to substances in your environment, such as dust mites, animal dander, pollen, and molds. Certain genes may also play a role in EoE.
Who is at risk for eosinophilic esophagitis(EoE)?
EoE can affect anyone, but it is more common in people who:
- Are male
- Have other allergic diseases, such as hay fever, eczema, asthma and food allergies
- Have family members with EoE
What are the symptoms of eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE)?
The most common symptoms of EoE can depend on your age.
In infants and toddlers::
- Feeding problems
- Vomiting
- Poor weight gain and growth
- Reflux that does not get better with medicines
In older children::
- Vomiting
- Abdominal pain
- Trouble swallowing, especially with solid foods
- Reflux that does not get better with medicines
- Poor appetite
In adults::
- Trouble swallowing, especially with solid foods
- Food getting stuck in the esophagus
- Reflux that does not get better with medicines
- Heartburn
- Chest pain
How is eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) diagnosed?
To find out if you have EoE, your doctor will likely:
- Ask about your symptoms and medical history. Since other conditions can have the same symptoms of EoE, it is important for your doctor to take a thorough history.
- Do an upper gastrointestinal (GI) endoscopy. An endoscope is a long, flexible tube with a light and camera at the end of it. Your doctor will run the endoscope down your esophagus and look at it. Some signs that you might have EoE include white spots, rings, narrowing, and inflammation in the esophagus. However, not everyone with EoE has those signs, and sometimes they can be signs of a different esophagus disorder.
- Do a biopsy. During the endoscopy, the doctor will take small tissue samples from your esophagus. The samples will be checked for a high number of eosinophils. This is the only way to make a diagnosis of EoE.
- Do other tests as needed. You may have blood tests to check for other conditions. If you do have EoE, you may have blood or other types of tests to check for specific allergies.
What are the treatments for eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE)?
There is no cure for EoE. Treatments can manage your symptoms and prevent further damage. The two main types of treatments are medicines and diet.
Medicines used to treat EoE are:
- Steroids, which can help control inflammation. These are usually topical steroids, which you swallow either from an inhaler or as a liquid. Sometimes doctors prescribe oral steroids (pills) to treat people who have serious swallowing problems or weight loss.
- Acid suppressors such as proton pump inhibitors (PPIs), which may help with reflux symptoms and decrease inflammation.
- Monoclonal antibodies, which can reduce inflammation and may help with swallowing. They can be used in adults and children over age 12.
Dietary changes for EoE include:
- Elimination diet. If you are on an elimination diet, you stop eating and drinking certain foods and beverages for several weeks. If you are feeling better, you add the foods back to your diet one at a time. You have repeat endoscopies to see whether or not you are tolerating those foods. There are different types of elimination diets:
- With one type, you first have an allergy test. Then you stop eating and drinking the foods you are allergic to.
- For another type, you eliminate foods and drinks that commonly cause allergies, such as dairy products, egg, wheat, soy, peanuts, tree nuts and fish/shellfish.
- Elemental diet. With this diet, you stop eating and drinking all proteins. Instead, you drink an amino acid formula. Some people who do not like the taste of the formula use a feeding tube instead. If your symptoms and inflammation go away completely, you may be able to try adding foods back one at a time, to see whether you can tolerate them.
Which treatment your doctor suggests depends on different factors, including your age. Some people may use more than one kind of treatment. Researchers are still trying to understand EoE and how best to treat it.
If your treatment is not working well enough and you have narrowing of the esophagus, you may need dilation. This is a procedure to stretch the esophagus. This makes it easier for you to swallow.
Source: MedlinePlus, National Library of Medicine.
MedlinePlus brings together authoritative health information from the National Library of Medicine (NLM), the National Institutes of Health (NIH), and other government agencies and health-related organizations.
Latest Update on Treatment Options
What Patients Should Know
Biologics
Dupilumab (Dupixent) is an injectable medication called a monoclonal antibody (or biologic) that is administered weekly. It reduces the inflammation associated with the disease and improves patients’ ability to swallow food. It is approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to treat people with EoE, ages 1 and older. This medication blocks the signaling of IL-4 and IL-13, two cytokines involved in inflammation. This medication may help improve dysphagia symptoms and be effective in patients who don’t respond to other therapies. Dupixent® is administered via a subcutaneous injection (under the skin). Source: Sanofi Regeneron
Topical Steroids
Budesonide Oral Suspension (EOHILIA) is the first and only FDA-approved oral therapy for people 11 years and older with eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE). EOHILIA is indicated for 12 weeks of treatment in adult and pediatric patients 11 years of age and older with eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE). Source: Takeda
Is Your EoE Well Controlled?
Shared-Decision Making Made Easy: Jump Start the Conversation with Your Healthcare Provider.
EoE Patient Guide
Are you living eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) and not responding to current treatment or dietary interventions? Not sure how to talk with your doctor about your symptoms or ask about other treatment options? Then this online tool is for you!
Your answers to these questions can help your healthcare provider better understand your symptoms and quality of life with EoE. Once you complete this brief questionnaire, your answers will be emailed to you for easy sharing with your healthcare provider.
Use this tool to prepare for a productive conversation with your doctor about:
- EoE symptoms
- Symptom frequency and severity
- Treatment goals
Listen to our
latest Podcast!