Hepatitis C

Summary
What is hepatitis C?
Hepatitis is inflammation of the liver. Inflammation is swelling that happens when tissues of the body are injured or infected. Inflammation can damage organs.
There are different types of hepatitis. One type, hepatitis C, is caused by the hepatitis C virus (HCV). Hepatitis C can range from a mild illness lasting a few weeks to a serious, lifelong illness.
Hepatitis C can be acute or chronic:
- Acute hepatitis C is a short-term infection. The symptoms can last up to 6 months. Sometimes your body is able to fight off the infection and the virus goes away. But for most people, an acute infection leads to chronic infection.
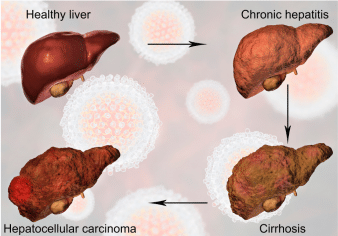
- Chronic hepatitis C is a long-lasting infection. If it is not treated, it can last for a lifetime and cause serious health problems, including liver damage, cirrhosis (scarring of the liver), liver cancer, and even death.
How is hepatitis C spread?
Hepatitis C spreads through contact with the blood of someone who has HCV. This contact may be through:
- Sharing drug needles or other drug materials with someone who has HCV. In the United States, this is the most common way that people get hepatitis C.
- Getting an accidental stick with a needle that was used on someone who has HCV. This can happen in health care settings.
- Being tattooed or pierced with tools or inks that were not sterilized after being used on someone who has HCV.
- Having contact with the blood or open sores of someone who has HCV.
- Sharing personal care items that may have come in contact with another person’s blood, such as razors or toothbrushes.
- Being born to a mother with HCV.
- Having unprotected sex with someone who has HCV.
Before 1992, hepatitis C was also commonly spread through blood transfusions and organ transplants. Since then, there has been routine testing of the U.S. blood supply for HCV. It is now very rare for someone to get HCV this way.
Who is more likely to get hepatitis C?
You are more likely to get hepatitis C if you:
- Have injected drugs
- Had a blood transfusion or organ transplant before July 1992
- Have hemophilia and received clotting factor before 1987
- Have been on kidney dialysis
- Have been in contact with blood or infected needles at work
- Have had tattoos or body piercings
- Have worked or lived in a prison
- Were born to a mother with hepatitis C
- Have HIV
- Have had more than one sex partner in the last 6 months
- Have had a sexually transmitted infection (STI)
- Are a man who has had sex with men (MSM)
If you are at high risk for hepatitis C, your health care provider will likely recommend that you get tested for it.
What are the symptoms of hepatitis C?
Most people with hepatitis C have no symptoms. Some people with acute hepatitis C do have symptoms within 1 to 3 months after they are exposed to the virus. These symptoms may include:
- Dark yellow urine
- Fatigue
- Fever
- Gray- or clay-colored stools
- Joint pain
- Loss of appetite
- Nausea and/or vomiting
- Pain in your abdomen (belly)
- Jaundice (yellowish eyes and skin)
If you have chronic hepatitis C, you probably will not have symptoms until it causes complications. This can happen decades after you were infected. For this reason, hepatitis C screening is important, even if you have no symptoms.
What other problems can hepatitis C cause?
Without treatment, hepatitis C may lead to cirrhosis, liver failure, and liver cancer. Early diagnosis and treatment of hepatitis C can prevent these complications.
How is hepatitis C diagnosed?
Providers diagnose hepatitis C based on your medical history, a physical exam, and blood tests.
If you do have hepatitis C, you may need additional tests to check for liver damage. These tests may include other blood tests, an ultrasound of the liver, and a liver biopsy.
What are the treatments for hepatitis C?
Treatment for hepatitis C is with antiviral medicines. They can cure the disease in most cases.
If you have acute hepatitis C, your provider may wait to see if your infection becomes chronic before starting treatment.
If your hepatitis C causes cirrhosis, you should see a doctor who specializes in liver diseases. Treatments for health problems related to cirrhosis include medicines, surgery, and other medical procedures. If your hepatitis C leads to liver failure or liver cancer, you may need a liver transplant.
Can hepatitis C be prevented?
There is no vaccine for hepatitis C. But you can help protect yourself from hepatitis C infection by:
- Not sharing drug needles or other drug materials.
- Wearing gloves if you have to touch another person’s blood or open sores.
- Making sure your tattoo artist or body piercer uses sterile tools and unopened ink.
- Not sharing personal items such toothbrushes, razors, or nail clippers.
- Using a latex condom during sex. If your or your partner is allergic to latex, you can use polyurethane condoms.
NIH: National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases
Source: MedlinePlus, National Library of Medicine.
MedlinePlus brings together authoritative health information from the National Library of Medicine (NLM), the National Institutes of Health (NIH), and other government agencies and health-related organizations.
Hepatitis C
National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases
Hepatitis C
American Academy of Family Physicians
Hepatitis C Basics
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
Hepatitis Panel
National Library of Medicine
Liver Function Tests
National Library of Medicine
Testing for Hepatitis C
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
5 Things You Should Know about Dietary Supplements for Hepatitis C
National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health
Complementary and Integrated Medicine for Hepatitis C
Department of Veterans Affairs
Hepatitis C and Dietary Supplements
National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health
Hepatitis C: Treatment
Department of Veterans Affairs
Listen to our
latest Podcast!